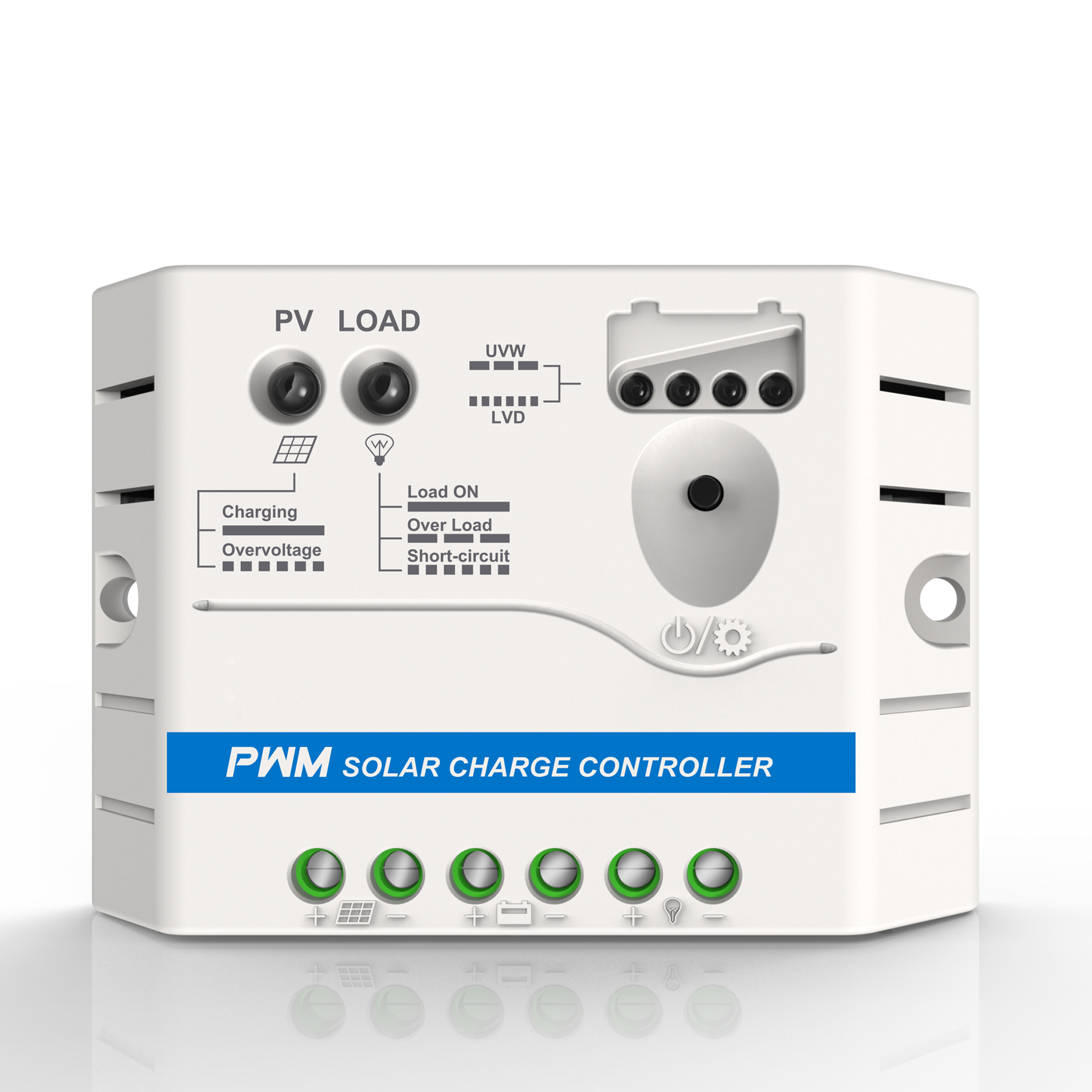
Bifacial solar panel
The front surface uses aluminum paste to print a fine grid similar to the front, and the back surface is covered by a partial aluminum layer instead of a full aluminum layer. The incident light on the back can enter the battery from the area not blocked by the Al layer, achieving a double-sided photoelectric conversion function, which is equivalent to increasing the light-receiving area of the battery, thereby increasing power generation. Similar to single-sided solar cell components, the back of the bifacial panel is also encapsulated with glass or a transparent backplane to optimize component performance while increasing the amount of light transmittance on the back.
Compared with single-sided solar cell components, bifacial components have further enhanced performance and applicability based on the advantages of zero water permeability, excellent mechanical properties, less hot spot damage, and low PID probability:
Low operating temperature reduces power loss. Temperature will affect the open circuit voltage, short circuit current, peak power and other parameters of solar crystalline silicon cells. When the temperature increases by 1℃, the peak power will be lost by 0.35% ~ 0.45%. The back side of the double-sided battery is made of highly transparent SiNx material. Infrared light can penetrate the battery and is not absorbed by the battery. The temperature under normal operation is 5~9°C lower than that of conventional components, reducing power loss.
Can be installed vertically, and the scope of application is expanded. Under reasonable installation inclination, height from the ground and ground reflectivity, the double-sided power generation module can make full use of the reflected light and scattered light in the environment to generate electricity. Therefore, in addition to traditional installation methods, bifacial power generation components can also be installed vertically, which is suitable for fences, solar curtain walls, highway sound insulation walls, lighting agricultural greenhouses and other occasions.
bifacial panel power generation gain 5%~30%
The performance of bifacial solar power plant system is mainly affected by the system design and installation environment. Under the same nominal peak power and installation location, the power generation gain of bifacial panel is 15%~20%; the gain can reach 30% after increasing the module height and ground albedo;
Gains even reach over 50% using oblique single-axis or tracking devices.
The efficiency of the back side of the solar cell is slightly lower than that of the front side. The light transmission on the back side leads to a slight decrease in the front side efficiency: since the laser opening point still requires a grid to guide the photogenerated current, most of the area on the back side of the cell is still covered with Al/Ag paste, and the aluminum grid The conductivity of the aluminum grid is not as good as that of the silver grid, so the aluminum grid lines are wider and the back coverage is as high as 30%~40%. Therefore, the area on the back that can absorb light is limited, and the conversion efficiency
(10%~15%) is significantly lower than the positive (more than 20%). At the same time, since the back side is composed of a full Al layer
If it is changed to partial coverage and the amount of light transmission increases, the front-side efficiency of the battery may decrease by 0.2-0.5%.
The power generation gain is affected by the reflective background, module orientation, installation angle, and ground clearance: the installation angle of double-sided power generation modules can be from 0° to 90°. The larger the angle, the greater the power generation gain compared to conventional modules; with tracking equipment such as tracking axes The power generation increases significantly; the lighter the background color, the higher the background reflectivity, and the greater the power generation increase; the higher the height above the ground, the larger the space between the module and the ground, and the larger the surrounding reflective surface that can be received by the back of the module. , the more power generated.